Posters/Publications
oral
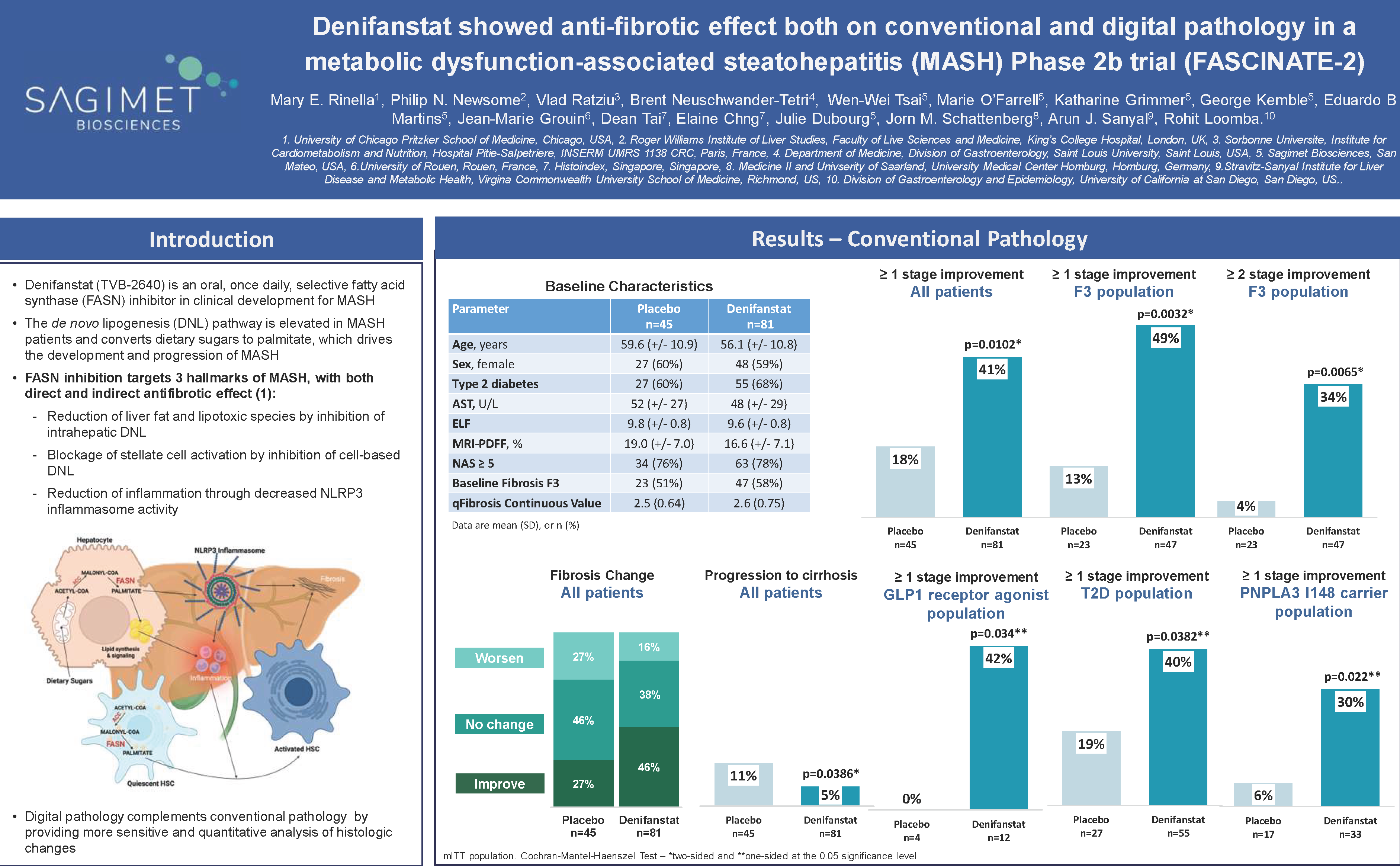
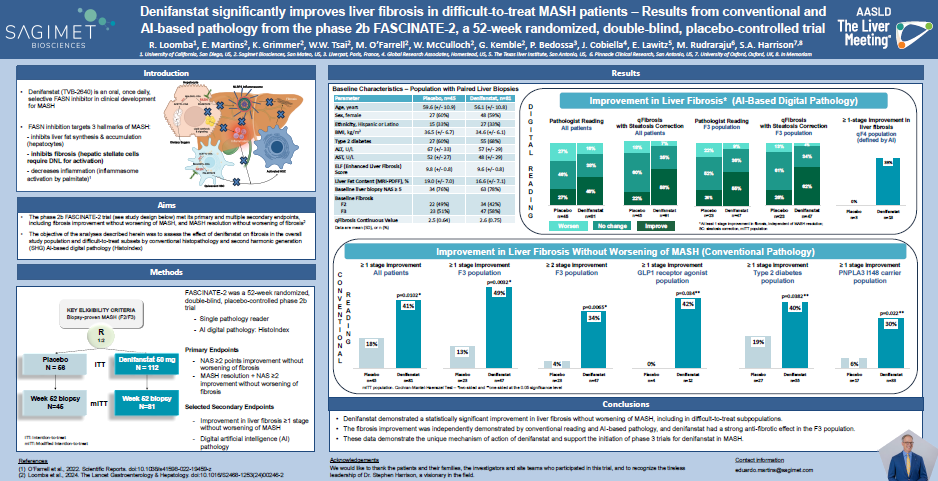
AI-Based Digital Pathology Shows that Denifanstat Improves Multiple Parameters of Fibrosis and Reduces Progression to Cirrhosis in MASH patients with F2/F3
AASLD The Liver Meeting
Date -
11/2024
poster
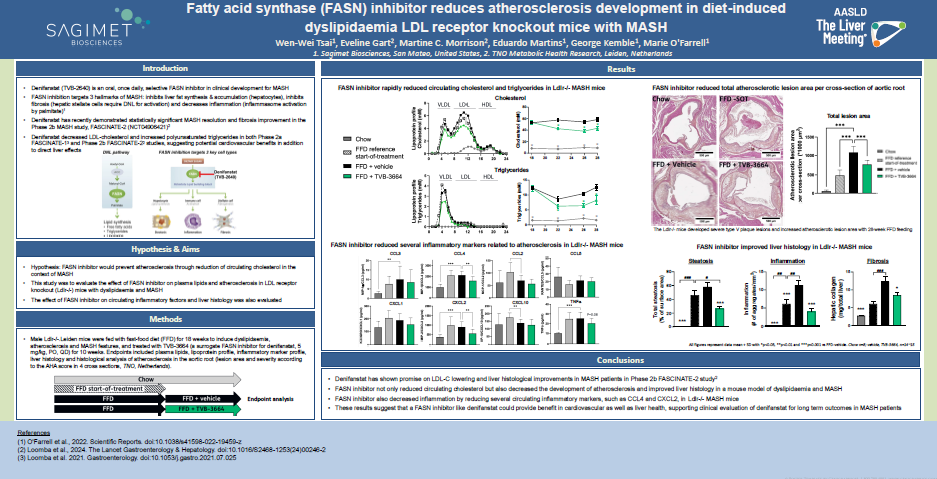
Fatty acid synthase (FASN) inhibitor reduces atherosclerosis development in diet-induced dyslipidaemia LDL receptor knockout mice with MASH
AASLD The Liver Meeting
Date -
11/2024
oral
Demonstrating denifanstat’s differentiated approach in MASH with mechanistic and clinical data showing direct anti-fibrotic activity
8th Annual MASH Drug Development Summit
Date -
09/2024